Are you afraid of eating fat? Don’t be!
Even though low-fat diets have been the craze for a long time, experts agree that it’s beneficial to consume healthy fat sources on a daily basis.
Fat is a macronutrient that has been misunderstood for some time, but we need it for energy, cell function, nutrient absorption, and much more.
While some people are unsure whether oil is good for you, it’s a no-brainer that we need to consume healthy vegan fat sources.

Types of fat
The quality of fat sources can differ widely, so we need to go over the different types of fat — and which you should emphasize — first.
Saturated fat
Mostly found in animal products but also in plant-based foods like coconut or palm oil, saturated fats (also called “solid fats”) are associated with a higher risk of heart disease.
Replacing this type of fat with healthier fat sources (see our list below) lowers your risk of heart disease!
Trans fat
Trans fat is the type of fat that is the worst for your health! It can increase your risk for many health problems and is often found in fried and processed foods such as cake mixes, shortening, donuts and pies.
Animal foods like red meat and dairy also have small amounts of trans fats.
download our free vegan nutrition printables
Grab your free PDF and sign up for our newsletter by entering your email below!
Monounsaturated fat
Monounsaturated fats are one type of “unsaturated fat” and are abundant in olive oil, canola oil, sunflower oil, avocadoes, and many nuts.
They are health-promoting and should be used to replace saturated fats!
Polyunsaturated fat
The other group of “unsaturated fat,” polyunsaturated fat, is also preferable and has a beneficial effect on your heart when eaten in moderation.
The two main types of PUFAs are omega-3 and omega-6, both of which are considered “essential,” — meaning we need to obtain them from our food.
Find excellent sources for these essential fatty acids in our following list!

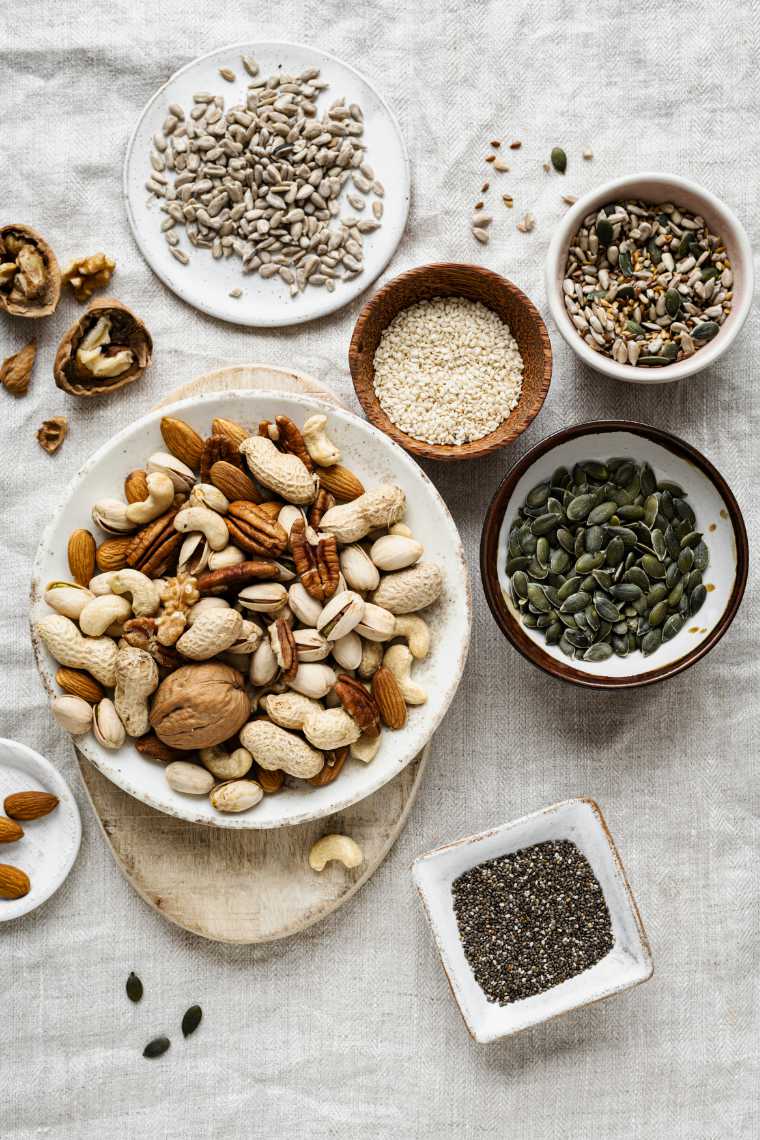
Healthy vegan fat sources
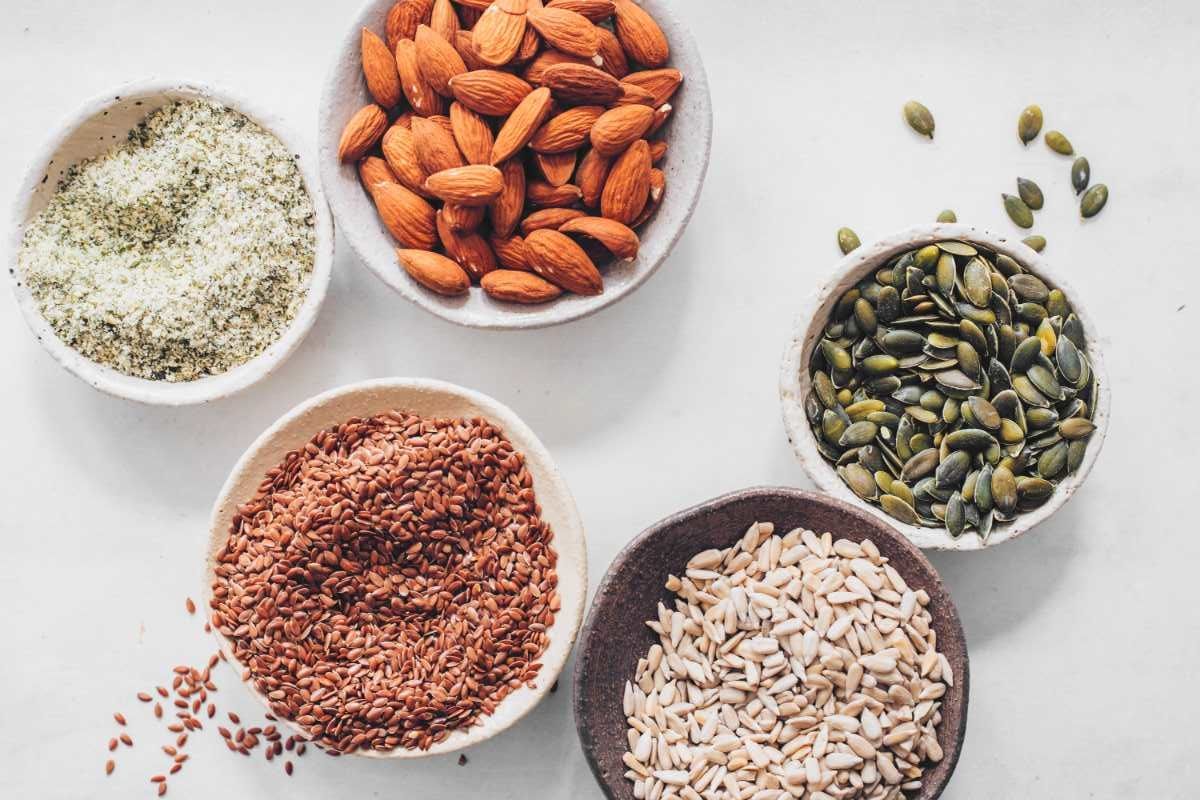
Nuts
Nuts are really crunchy, nutrient-dense, and offer a good amount of fiber, plant-based protein, and unsaturated fats.
We love this versatile, healthy fat source in our oatmeal, granola, energy balls, and salad, made into almond creamer or vegan cheese. Don’t forget about peanut butter, too!
Some nuts deserve honorable mentions because they are especially good for you!
- Walnuts (omega-3)
- Almonds (vitamin E)
- Brazil nuts (selenium)
- Pecans (manganese)
- Peanuts (vitamin B3 & protein)
Seeds
Seeds are arguably even healthier than the popular walnuts, almonds, or peanuts because they are packed with potentially critical nutrients for vegans (and other eaters.)
The same is true for seed butter made from sesame seeds, pumpkin, or sunflower seeds.
Full of monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, you can enjoy seeds and seed butter in various ways: salad topping, tahini dressing, energy balls, overnight oats, smoothies, or to make your own protein powder.
Some seeds deserve honorable mentions because they are especially good for you!
- Flax seeds (omega-3)
- Chia seeds (omega-3)
- Hemp seeds (omega-3)
- Pumpkin seeds (zinc)
- Sesame seeds (calcium)
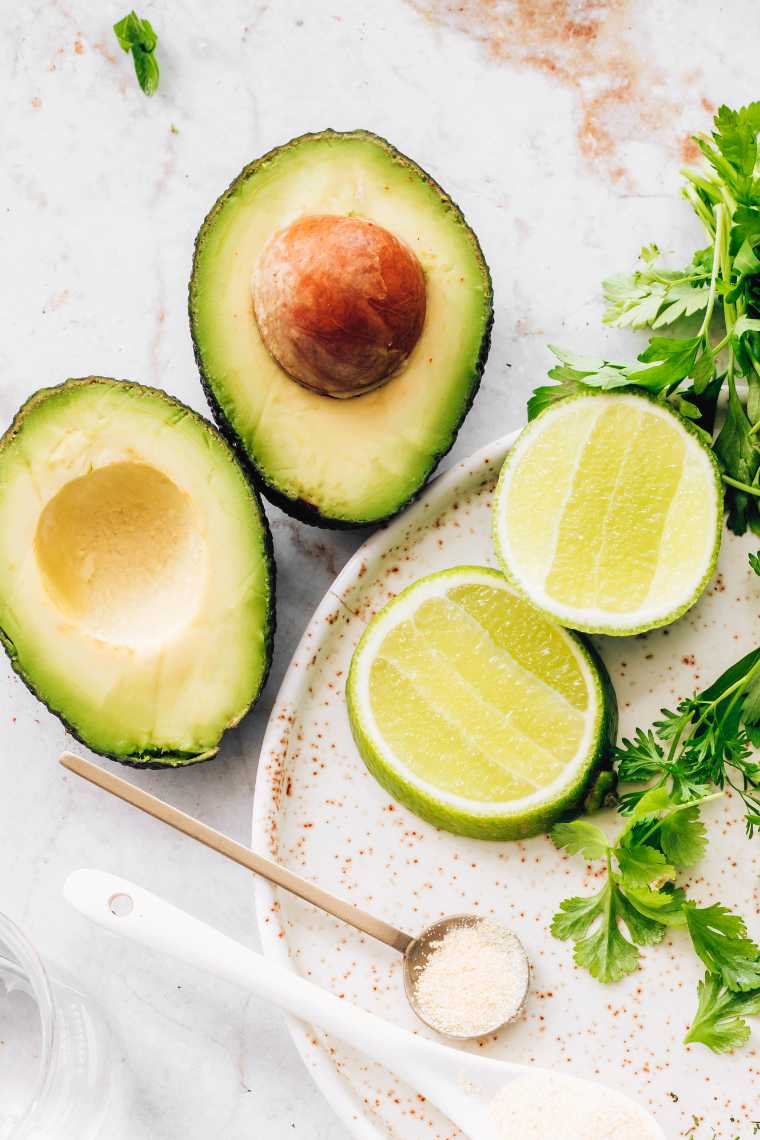

Avocado
Native to Mexico and Central America, avocadoes are enjoyed in almost every country worldwide.
While some environmentally conscious people try not to eat them too often, they are a fantastic source of healthy fats, vitamins E & K, folate, and fiber!
Compared to other higher-fat foods, they aren’t as high in calories and are our favorite vegan butter replacement on toast.
Make them into guacamole and add them to burritos or veggie bowls!
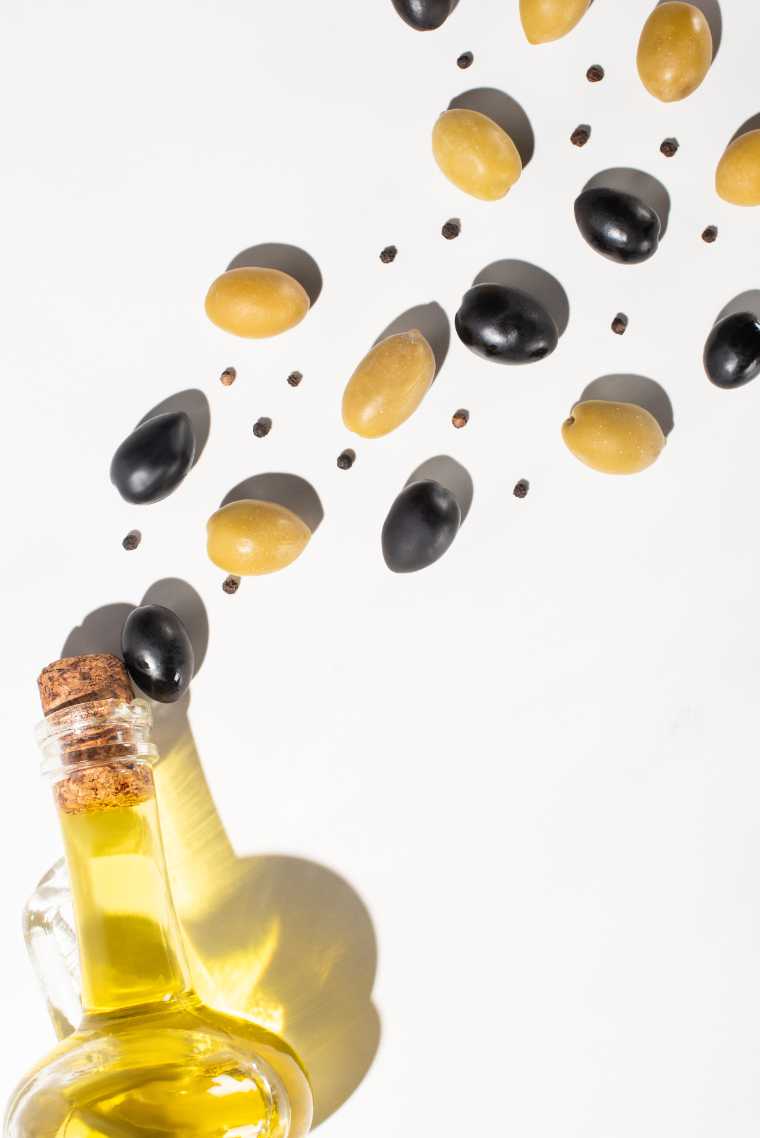
Olives
Like avocados, olives are actually a fruit with lots of antioxidants, fiber, and vitamin E. Olives contain 11-15% fat, most of which is monounsaturated.
An essential component of Mediterranean cooking, they are often enjoyed in salads, sandwiches, or tapenades.
One side note: olives are typically high in salt because they are cured or packaged in brine or salty water, so enjoy them in smaller amounts!
Olive oil
Extra-virgin olive oil is made from pure, cold-pressed olives, and, therefore, also high in unsaturated fat.
Regular olive oil is also considered healthy and can be used for lower-temperature cooking or salad dressings. Read our full article on olive oil here!

Flaxseed oil
Flaxseed oil is made from ground and pressed flax seeds and high in omega-3s and health-promoting lignans.
It may improve heart and gut health but should only be consumed in cold dishes and stored in the fridge!
Dark chocolate & cocoa powder
Do you love reading good news about chocolate? Well, we certainly do!
Adding cocoa powder to smoothies or oatmeal isn’t just delicious, but it can also bump up your daily mineral intake.
If you love snacking on dark chocolate (70-85% of cocoa), you can get fiber, iron, magnesium, copper and manganese with each bite!
However, this shouldn’t be your primary source of essential nutrients because the calories add up quickly.
Coconut
Coconut products range from coconut meat and flakes to coconut milk, oil, and water.
While coconut oil is really high in saturated fats and shouldn’t be used in larger amounts, coconut meat contains fiber, manganese, copper, and some iron.
It is lower in fat than coconut oil and can be used to make vegan bacon, added to curry, baked goods, smoothies, or porridge.
Soy
You might be surprised to read that tofu, tempeh and other soy products are a good source of fat!
While most other legumes like black beans, chickpeas or lentils are pretty low in fat, it’s a different story for soy.
100 grams offer 17 grams of protein and 9 grams of fat — most of which is unsaturated. Soy products are often a good source of calcium, too!
Is Soy Good For You? →
Oats, buckwheat & quinoa
These items might surprise you, but some grains aren’t just full of complex carbs — they also have decent amounts of plant-based protein and healthy fats!
Primarily, they are excellent sources of fiber and perfect for people on a gluten-free diet. They can also slow your fat absorption while providing around 17% of their calories from mostly omega-6 fatty acids.
Durian
This unique tropical fruit native to Southeast Asia is high in nutrients (including fat!) and features a strong smell.
You can find it in Asian supermarkets and add it to soups or use it to make desserts!
The flavor of Durian is described as tasting like cheese, almonds, garlic, and caramel all at once — you either really love or really don’t like it.
More vegan guides
If you liked this article, check out the following ones next!
- Vegan Food Pyramid
- Low-Carb Vegan Diet
- How to Gain Weight as a Vegan
- Healthy Food Swaps
- High-Calorie Vegan Foods
What are your favorite vegan fats? Let us know in the comments below and don’t forget to Pin this article here!






 Alena Schowalter is a Certified Vegan Nutritionist who has been a vegetarian since childhood and vegan since 2012. Together with her husband, she founded nutriciously in 2015 and has been guiding thousands of people through different transition stages towards a healthy plant-based diet. She’s received training in the fields of nutrition, music therapy and social work. Alena enjoys discussions around vegan ethics, walks through nature and creating new recipes.
Alena Schowalter is a Certified Vegan Nutritionist who has been a vegetarian since childhood and vegan since 2012. Together with her husband, she founded nutriciously in 2015 and has been guiding thousands of people through different transition stages towards a healthy plant-based diet. She’s received training in the fields of nutrition, music therapy and social work. Alena enjoys discussions around vegan ethics, walks through nature and creating new recipes.
Add these delicious and healthy vegan fats to your meals and create a well-rounded plant-based diet! Read about different types of fatty acids & find easy recipes.